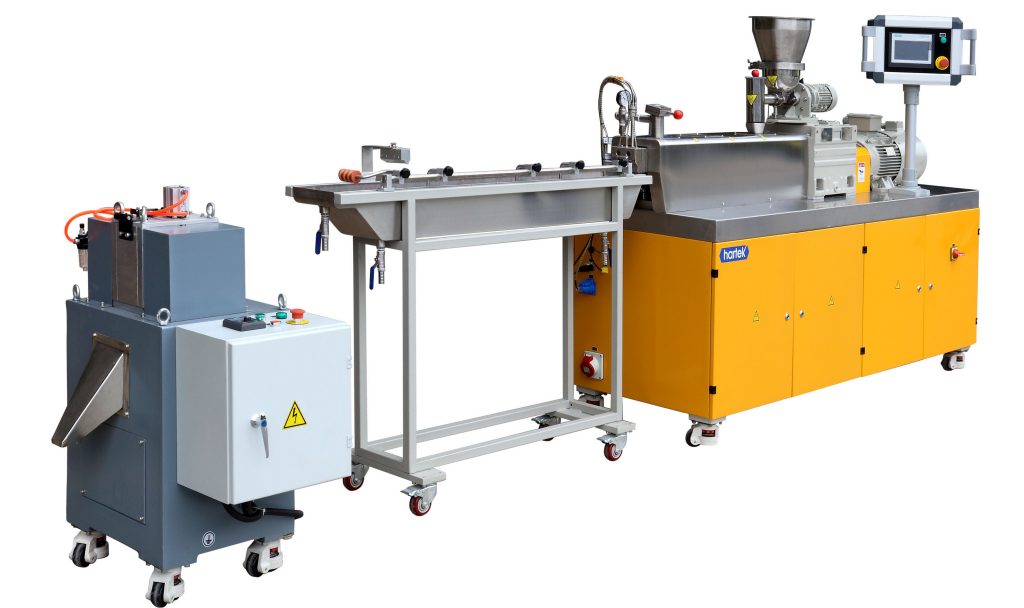
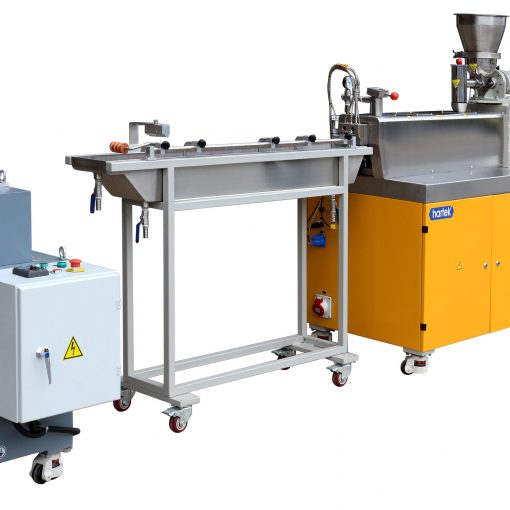
Classification of twin screw extruder
According to the rotation direction of the twin screw, the extruder can be divided into two types: co-direction and counter-direction extruder. The co-direction extruder is the same rotation direction when the two screws work. The direction of rotation is reversed during operation.
According to whether the axis of the twin screw is parallel or not, it can be divided into two types of extruders whose axis is parallel and the axis intersects. A twin-screw extruder with parallel axis lines and a conical twin-screw extruder with axis centers intersecting.
Twin-screw extruders are also distinguished between intermeshing and non-engaging.
The parallel and conical twin-screw extruders are the same: they have a forced forward conveying mechanism for plastics, good mixing and plasticizing capabilities and dewatering capabilities, and they have basically the same adaptability to the molding process of materials and plastic products.
Differences between parallel and conical twin screw extruders
- Diameter: The diameter of the parallel twin screw is the same, the diameter of the small end of the conical twin screw is different from the diameter of the big end.
- Concentric distance: The center distance of the flat twin screw is the same. The two axes of the conical twin screw are at an angle. The size of the center distance varies along the axis.
- L / D ratio: Parallel twin screw (L / D) refers to the ratio of the effective part length of the screw to the outer circle of the screw. Conical twin screw (L / D) refers to the effective part length of the screw and the large-end diameter and small The ratio of the average of the end diameters.
From the above, we can clearly see that the most significant difference between parallel and conical twin-screw extruders is the geometry of the screw barrel, which causes many differences in structure and performance. Although the characteristics of the two are different, But each has its own advantages.
Parallel twin screw extruder
Due to the small size of the center distance between the two screws, in the transmission gearbox, there is limited space for the radial and thrust bearings and related transmission gears that support the two output shafts. Although the designer has exhausted his efforts, it cannot solve the problem. The bearing capacity, the modulus of the gear, the small diameter, and the small diameter of the two screw tails result in poor torque resistance. Small output torque and poor load resistance are the most significant defects of parallel twin-screw extruders. However, the plasticity of the aspect ratio is the advantage of the parallel twin screw. It can increase and decrease the aspect ratio to meet the requirements of the plastic processing technology according to the difference in molding conditions. It can expand the scope of application of the parallel twin screw, but this point is tapered. Twin screw extruder is difficult to do.
Conical twin screw extruder
The two conical screws are arranged horizontally, and the two axes are inserted into the barrel at an angle. The center distance between the two axes gradually increases from the small end to the large end, so that the two output shafts of the transmission gearbox have a larger center distance. The gears and gear shafts in the transmission system and the radial and thrust bearings that support these gear shafts have a large installation space. It can install larger specifications of radial and thrust bearings. Each transmission shaft is sufficient to meet the transmission torque. The diameter of the shaft, so the large working torque and load capacity are a major feature of the conical twin-screw extruder. This parallel twin screw extruder is incomparable.